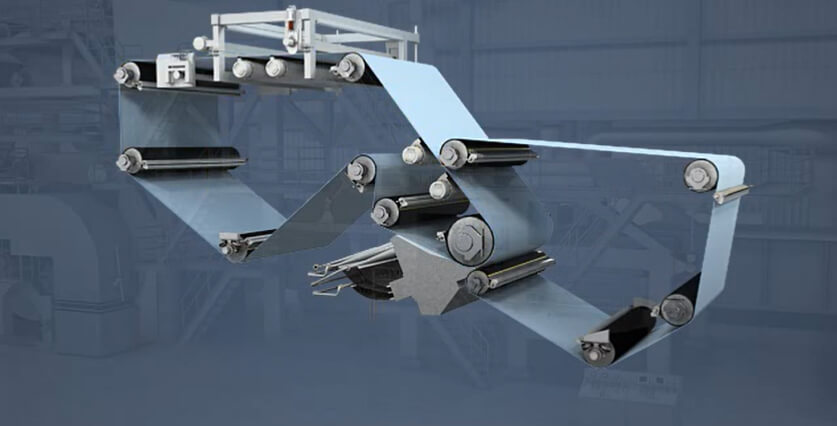
What is Forming Fabrics?
In the forming section of the paper machine, a mixture of approximately 99% water and 1% cellulose fibers and filler material is introduced uniformly across the width of the forming fabric. During this process, the forming fabric acts as both a conveyor belt and a dehydrator. When the fabric moves quickly, more than 96% of the water is drained through the special voids in the fabric, while the fibers and fillers remain on top of the fabric to form a paper sheet structure. PFM SCREEN's forming fabrics provide a stable, durable environment in the process. PFM SCREEN has constantly improved their forming fabric technology and created fabrics providing excellent runnability, high wear resistance, long running time, good paper profiles and good retention.
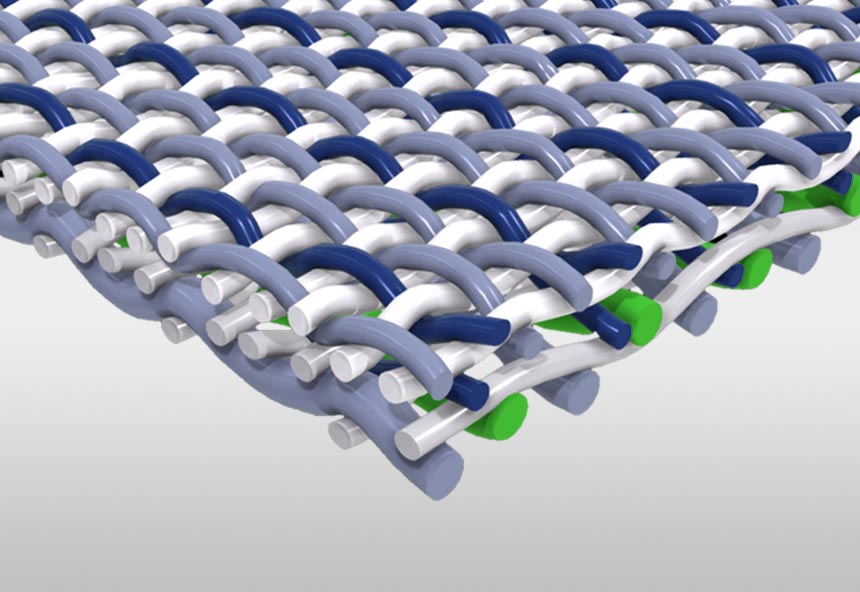
Available materials for forming fabric yarns
The main raw material of forming fabric is polyester or nylon monofilament, and polyester monofilament is the most widely used material. Compared with other synthetic polymer materials, it has the following advantages:
High load elasticity, strong dimensional stability, strong and durable.
Smooth surface, strong anti-fouling ability, easy to clean.
High fatigue resistance.
Corrosion resistance, excellent acid resistance.
Minimal hygroscopicity and high stability in humid environment.
In some cases, the addition of nylon can greatly improve the properties of forming fabrics. Although nylon is less stable (due to its hygroscopic properties), it has better abrasion and alkali resistance than polyester.

Monofilament diameters used to produce forming fabrics are typically between 0.1 and 0.5 mm.
| Polyester | Polyamide(Nylon) |
| Tensile Strength | 35-70 N/mm2 | 28-46 N/mm2 |
| Elongation | 16-40% | 20-70% |
| Specific Gravity | 1.38 | 1.14 |
| Moisture Absorption 24hr | 0.20% | 2.90% |
| Temperature Limit in Use | 140° | 90-130°C |
| Effects of Acids | It is very stable to organic acids. After soaking in hydrochloric acid solution and dilute sulfuric acid, its strength is not lost, but it cannot resist the long-term action of concentrated nitric acid or concentrated sulfuric acid. | Decomposes when boiled with 5% hydrochloric acids; also affected by other acids |
| Effects of Alkalis | Resistant to weak bases, easily hydrolyzed under the action of strong bases | Unchanged in all alkaline environments |
The weaving process of forming fabrics
Paper forming fabrics are high-tech fabrics woven through a series of high-tech equipment and strict production inspection procedures. In order to produce high-quality paper forming fabrics, most of PFM SCREEN's production equipment is imported from Europe, including Sweden TEXO 13.5 Meters Weaving Machine, Austrian WIS Automatic Seaming Machine, Germany Jurgens 16 Meters Weaving Machine, and so on.
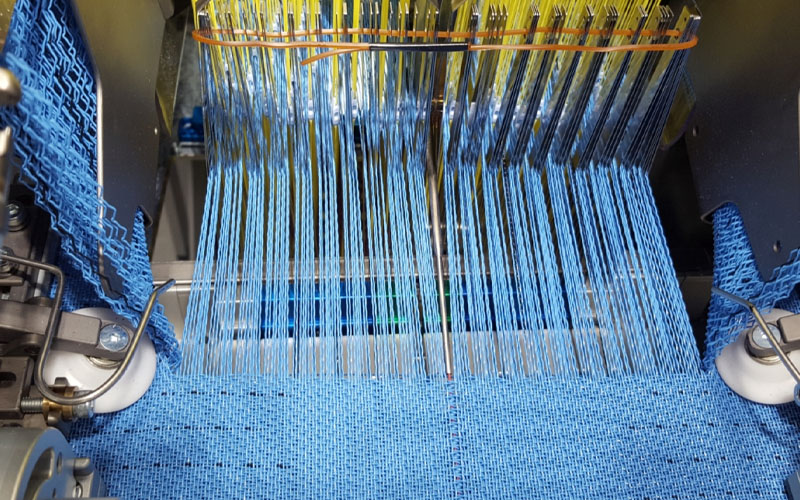
Warping
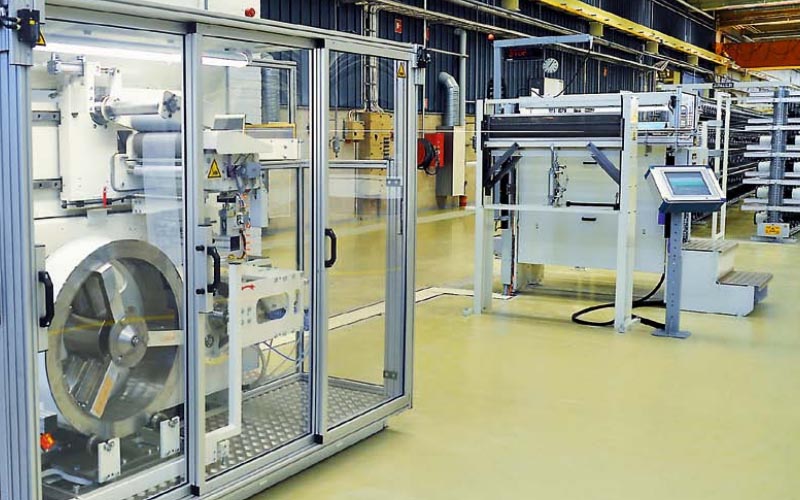

The forming fabric is made up of two sets of yarns, warp and weft. The warp runs along the length of the forming fabric and the weft runs across the width of the forming fabric. Warping is the preparation of yarns for weaving fabrics. It is the transfer of many yarns from the creel of a single package to the beam. The yarns will form parallel yarn sheets wound on the beam. The basic goal of warping is to build a package that keeps the yarn ends in a uniform parallel and continuous pattern, thereby speeding up the next process.
lnspection
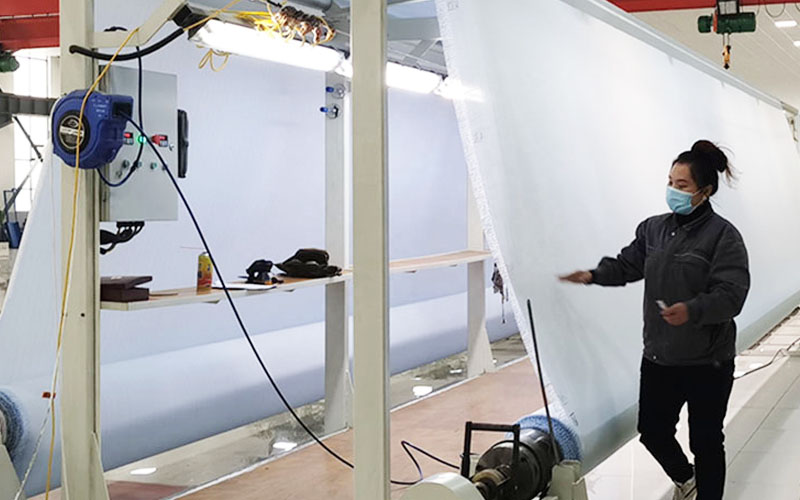

Check the fabric surface for imperfections
Remove contaminants such as dust or grease
Heat setting
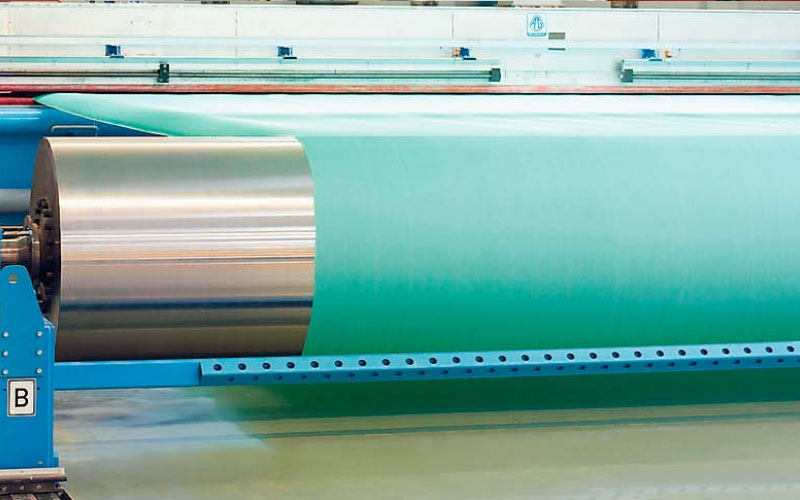

Heat setting is a heat treatment method for textiles, through which the shape retention, wrinkle resistance, resilience and elasticity of polymer polyester fiber fabrics can be enhanced. Heat setting also brings about changes in fabric strength, stretch, flexibility and dyeability.
The heat setting process stabilizes the forming fabric warp and weft material through the action of tension and heat, homogenizes the forming fabric structure and eliminates internal tension within the fibers, thereby reducing shrinkage, improving dimensional stability and reducing wrinkles in forming fabrics tends and reduces edge curl.
Seaming

The forming fabric runs continuously at high speed in the forming section of the paper machine as an endless belt. However, forming fabrics woven by looms are often sheet-like and require the use of a seaming machine to join the ends together. Seam flatness and strength are critical to paper quality and forming fabric durability. PFM SCREEN has introduced the most advanced automatic seaming machine from Austria WIS, which is used for endless seaming of forming fabrics, which not only improves production efficiency, but also ensures high-quality forming fabric.
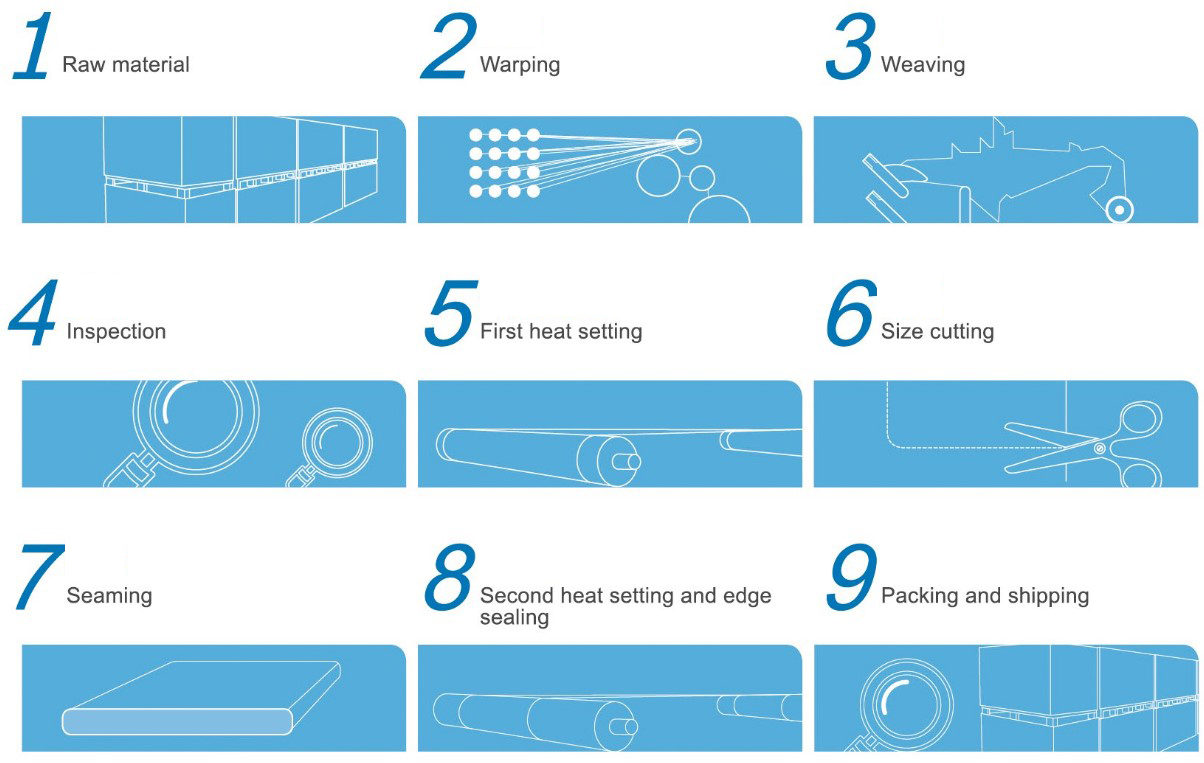
Packaging

The packaging of the forming fabric is equally important. Improper packaging may cause wrinkles or even breakage of the forming fabric. PFM SCREEN has formulated strict packaging process and requirements, including the rolling method of forming fabric, the threading method of paper tube, scratch-resistant protective film and wooden box, etc. Finally, the outer packaging of each forming fabric will paste its detailed usage information according to customer requirements.
Classification of forming fabrics
There are many types of forming fabrics, and international classifications are also different. At present, it is roughly classified according to weaving method, wire structure, and fabric level.
1. Distinguish by weaving method
(1) Ring woven forming fabric (also called endless forming fabric). The forming fabric is woven into a loop on the weaving machine without seams, but the equipment required is huge. Because the perimeter of the wire required by the paper machine varies, the polyester forming fabrics currently used on the paper machine are all sheet-woven nets.
(2) Piece weaving forming fabric. The piece woven forming fabric is also called a terminal forming fabric or a plug-in forming fabric. According to the requirements of the paper mill, the two ends of the forming fabric are inserted with a width of 10-15 cm to form a ring-shaped forming fabric with joints, which are then subjected to heat setting.
2. Distinguish by wire structure
(1) Monofilament. The wire material of the forming fabric is a single filament, which is a single filament of various diameters made from a synthetic material after being drawn. Monofilament has excellent abrasion resistance, tensile strength and is very strong. Polyester monofilament is the main raw material for weaving various forming fabrics.
(2) Multifilament. Good water absorption and strong tension resistance.
(3) Interwoven mesh fabric. The so-called interwoven mesh fabric is a mesh fabric woven with two kinds of wires: multifilament and monofilament. Generally use multifilament for warp and monofilament for weft, or use monofilament for warp and multifilament for weft.
3. According to the fabric layer
(1) Single layer forming fabric
(2) Double-layer forming fabric
(3) 2.5 layer forming fabric
(4) Triple-layer forming fabric
4. According to the weaving type, polyester forming fabrics can be divided into 4-shed, 5-shed, 8-shed, 16-shed, 24-shed, etc.
5. According to the sliding of the forming fabric wires, it is divided into a warp sliding forming fabric and a weft sliding forming fabric.
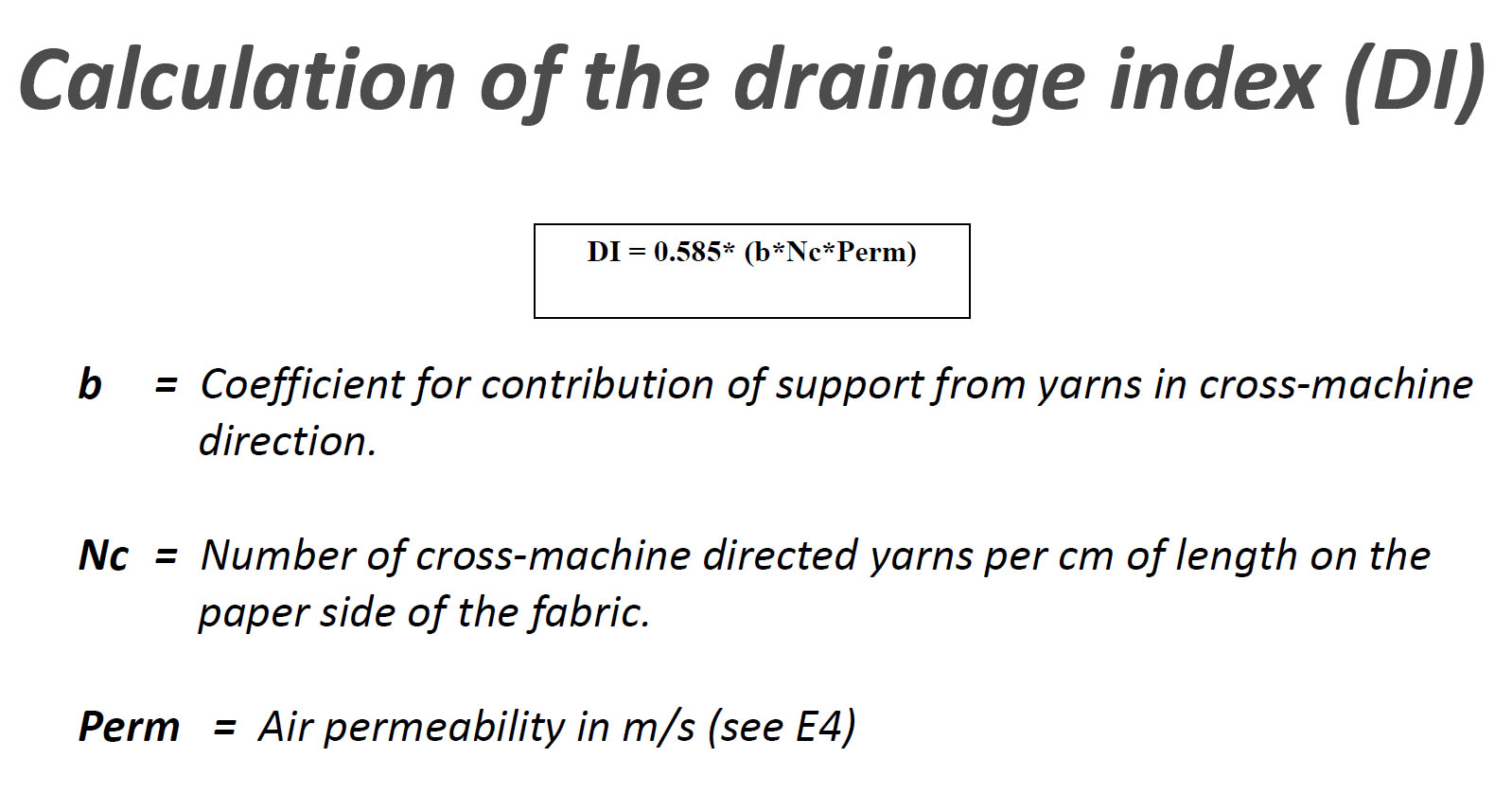
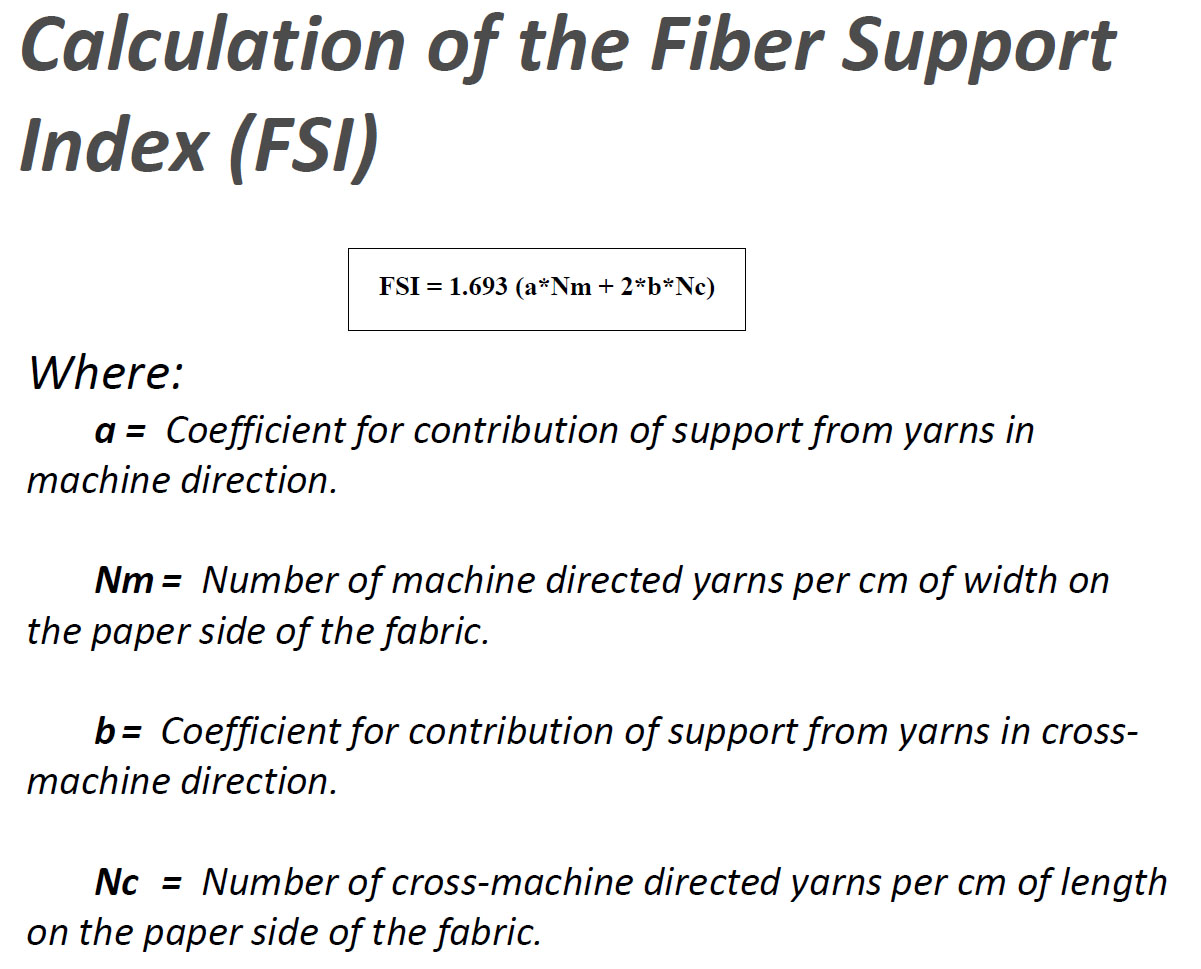
Main performance parameters of forming fabrics - Fiber Support Index (FSI) - and Drainage Index (DI)
The Fiber Support Index (FSI) and Drainage Index (DI) were often used to evaluate the performance of forming fabric.
The Drainage Index (DI) indicates the drainage performance of the formed fabric. For forming fabrics, the higher the drainage index, the better the rapid dewatering of pulp in the forming section. About 0.4%~1% of the pulp is fiber structure and the rest is all water. In the papermaking forming section, the more water is discharged in a short time, the better, and the more beneficial to the paper forming and subsequent sections of papermaking.
The ability of the forming fabric to support the fibers in the pulp is expressed by the Fiber Support Index (FSI). A high-quality forming fabric not only needs to drain moisture quickly, but it must also have good fiber support on its surface to form a high-quality paper sheet. The good fiber support properties of the forming fabric can not only improve the flatness, smoothness, printability and strength properties of the paper sheet, but also prevent the forming fabric from being embedded or blocked by pulp fibers.
How to choose the right forming fabric for your paper machine
The type, length and width of the forming fabric are usually selected according to the type of paper machine and the composition of the pulp.
1. Selection of forming fabric models. It is determined according to the characteristics of the paper machine and the type of paper, and at the same time, conditions such as pulp properties, fillers, and rubber materials should also be considered. The selected forming fabric should make the screen printing light, the paper surface smooth and smooth, and the dewatering performance is good.
| Paper Grade | Single-layer | Double-layer | Triple-layer |
| 1.5-layer | 2.5-layer | Triple Weft-layer |
| Newsprint |
| √ | √ |
| Fine paper | √ | √ | √ |
| Brown & Kraft | √ | √ | √ |
| Tissue paper | √ | √ |
|
| DNT Washer |
|
| √ |
| Shrink Sleeves | √ |
|
|
2. Selection of the length of the forming fabric. The characteristics of polyester materials are that the forming fabric will stretch under the action of the bearing force. The extent of elongation varies with the molecular weight of the material, the degree of heat setting and the weaving method. For example, the elongation of a single-layer forming fabric is generally It is larger than the multi-layer forming fabric, the plug-in endless fabric is larger than the loop woven fabric, the elongation of the low molecular weight is greater than that of the high molecular weight, etc., but the maximum elongation is not more than 1.3%, and the minimum elongation is not less than 0.3%. Therefore, to properly use polyester forming fabrics, the length of the forming fabric must be carefully checked. The maximum elongation of the forming fabric during operation is about 1%. Due to the high elasticity of the forming fabric, there is elongation at the beginning of use, and then the elongation becomes smaller. The length elongation of the forming fabric at the beginning of the operation is the best at 0.5%.

In order to ensure the proper use of the forming fabric, it is important to determine the minimum and maximum running lengths of the forming fabric loops. Generally, the length of the forming fabric should be determined as short as possible, as long as the forming fabric can be easily put on the paper machine, but the length of the forming fabric must be finally determined by actual measurement. It is proper about 5-10 cm greater than the fabric minimum running length on the forming section or the minimum installation length can be guaranteed. This avoids the situation that the fabric is not tight at the end of the period.
3. Selection of forming fabric width. The width of the forming fabric is based on the model of the paper machine and the specifications of the sheets produced. It is necessary to ensure that the wet paper has a shrinkage range that meets the process conditions, and pay attention to factors such as wet paper edges and burrs. To prevent fraying and unraveling, a soft resin is impregnated into the edges of the fabric.

