
Paper making process, usually out of the flow box pulp concentration of about 0.3% to 1.0% (when copying packaging paper out of the flow box pulp concentration of up to 1.6%), the paper web leaves the net into the press section before the dryness of 18% to 23%, high-speed paper machine up to 27%, that is, 95% of the water removal in the papermaking process is completed in the net. Paper forming nets run on each roll and dewatering plate, wear relatively serious, is the main special dewatering and consumption equipment for papermaking. With the increasing demand for paper quality, as well as modern paper production gradually to the direction of wide, high-speed and low quantification, paper forming fabrics must adapt to the modern high-speed paper machine requirements such as efficient, uniform and stable dewatering. In addition to excellent fiber retention characteristics, efficient dewatering performance and good cleaning effect, the paper forming fabric also needs to have good operational stability. At present, the polyester forming fabric has almost completely replaced the traditional copper forming fabric, especially the polyester three-layer forming fabric has become the mainstream forming fabric for modern paper machines.
Ancient papermaking is represented by the invention of the Chinese Eastern Han Cai Lun manual paper copying, the use of bamboo silk woven bamboo curtain sieve or lined with a backing of the wooden frame for paper copying. With the introduction of paper technology to the West, especially the industrial revolution caused by the invention of the paper machine, metal (mainly copper or stainless steel) paper forming mesh gradually replaced the bamboo mesh sieve. Paper machine speed and width of the expansion, metal forming net load heavy, short life and poor acid and alkali resistance and other shortcomings are increasingly obvious, gradually replaced by plastic forming net. Plastic mesh is also divided into polyester mesh, polyamide (nylon) mesh, polypropylene mesh, etc.. Polypropylene net is not easy to absorb water, small density, stable form, acid and alkali resistance, but its easy aging, wear resistance is poor, the use of slightly lower temperature, the use of limited; polyester net and nylon net comprehensive performance is good, polyester net form stability is good, nylon net wear resistance is strong, most of the current forming net is polyester forming net, in the bottom layer of multi-layer polyester net with a certain ratio of nylon net, to improve its wear resistance.
Polyester and nylon are synthetic polymers, you can add different additives and use different modification methods to improve the characteristics of polyester and nylon fibers according to demand, in order to adapt to the operation of high-speed modern paper machines, is currently multi-layer polyester forming fabric is the most commonly used material. Polyphenylene diamide (PPA) is a compound of polymer formed by condensation between isophthalic acid, terephthalic acid, adipic acid and hexanediamine, a semi-crystalline semi-aromatic nylon. ppa has good heat resistance, excellent mechanical properties and dimensional stability, low water absorption and excellent molding processability, chemical resistance, etc. PEEK monofilament is a thermoplastic polymer, is the most advanced Stabilon is a new monofilament material, the same wire diameter Stabilon monofilament has 30% higher modulus of elasticity than polyester monofilament. In addition, the monofilament for multi-layer bottom net has the stability of polyester and the abrasion resistance of nylon, and the service life of this net reaches 90 days, while the forming net using a mixture of polyester and nylon is only 42 days on average, with the longest being 73 days. It can also consider the application of nanotechnology and fiber surface modification to improve the performance of forming nets such as dehydration and wear resistance.
As the modern paper machine to large-scale, high-speed and automated development, and thus the metal forming network can no longer adapt to the requirements of modern paper machine. Along with the development of polymer synthesis technology, many high-performance plastic polymer materials have been introduced, the middle of the 20th century, paper forming network gradually transitioned from copper to synthetic polyester fiber woven forming network. Polyester and other synthetic materials for paper forming net, for the paper machine to high-speed, wide-width development has epoch-making significance. Compared with copper and other metal forming net, polyester forming net has the following advantages: small density, small paper machine load, high production efficiency; soft material, easy to operate, not easy to bruise; corrosion resistance, wear resistance, service life is generally 3 to 5 times longer than copper, or even longer; can improve the evenness of paper, reduce network traces and two-sided difference, improve smoothness and reduce the loss of fibers and fillers, can reduce the number of times to change the net as well as due to change the net brought Polyester forming fabric weaving methods are more flexible, can use different weaving methods and change the number of layers of forming fabric to meet the different paper machine, different paper types and different paper conditions, in order to improve the operating efficiency of the paper machine. Polyester forming fabric is also divided into single-layer and multi-layer fabric.
Polyester forming net is originally woven according to the weaving process of copper net single-layer net, but the wire from copper wire to polyester wire, making its quality lighter, thereby reducing the transmission load of the paper machine, saving paper costs. Single-ply fabrics are made by interweaving a single weft system and a single warp system. Single-ply webs are relatively simple to weave, such as four heddle single-ply webs where the curved weft threads pass under 3 warp threads and over 1 warp thread, while the warp threads pass over 3 weft threads and under 1 weft thread, protecting the warp threads, which are under tension load, from being inside the structure of the web, while leaving the weft threads in contact with the various friction parts of the paper machine. Fine polyester monofilament can weave high-density warp and weft structure of the single-layer net, fiber and filler retention rate is high, suitable for the production of paper sheet surface performance of good paper; this kind of net weft is relatively thin, not wear-resistant, short service life. The coarse polyester monofilament woven single-ply net with low density warp and weft structure can improve the abrasion resistance and service life of the forming net, but its fiber and filler retention rate is low and the paper-forming performance is poor. The improved reinforced single-layer net is characterized by the addition of a group of smaller diameter weft threads on the basis of the ordinary single-layer net, and this group of fine weft and thicker weft threads are alternately interwoven with the warp threads, the purpose of which is to enhance the lateral stability, increase the fiber and filler retention rate and improve the paper formation performance. This kind of forming network in the speed of 200m/min or less, the width of the narrower paper machine applications more. For high-speed paper machine, single-layer forming network can not meet the requirements.
Modern high-speed wide paper machine requirements forming network has a good dewatering effect and high fiber, filler retention rate, single-layer forming network (including reinforced) can not meet the demand. In order to meet the requirements of modern high-speed, wide-web paper machines, multi-layer polyester forming fabrics have been developed. The advantage of multi-layer fabrics is that the performance of the top (paper side) and bottom (machine side) layers of the forming fabric can be improved through the separate design of the top and bottom layers of the woven structure to better suit the needs of various paper machines. The idea is that the top layer has a higher fiber support index (FSI) while ensuring dewatering, while the bottom layer enhances the bottom weft resistance to abrasion while ensuring a smooth dewatering channel. Currently, two-ply, two-and-a-half-ply, three-ply and three-and-a-half-ply series have been maturely applied and are woven with different heald numbers to achieve the required properties.
According to the previous idea, two-ply nets are woven on the basis of single-ply forming fabrics and are designed relatively independently by introducing multiple weft systems in the lateral direction, depending on the function of the face and bottom layers. From the lateral (CD) structure of the two-layer net, there are two independently separated weft systems - the face weft and the bottom weft - which realize their different functions, and the warp threads are also of two layers. The weaving process is that the same warp thread passes through the upper weft thread and then down through the lower weft thread, so that the top and bottom layers are woven together. Compared with single-ply webs, this two-ply structure is denser and more stable in size, and can be adapted to the requirements of different paper machines by changing different weaving processes. Generally, the density and wire diameter of the top and bottom weft are different. The density of the top weft is slightly larger and the wire diameter is smaller, which is conducive to improving the retention of fibers and reducing the difference between the two sides of the paper; the wire diameter of the bottom weft is thicker, in order to make the net more wear-resistant and improve the service life. The lack of stiffness and poor lateral stability of this type of two-ply net restricts its application on high-speed wide-web paper machines. For this reason, researchers have developed a reinforced two-ply net (three-ply weft net). It is a variation form of the traditional two-ply net. Although this type of net improves stiffness and lateral stability, the overall compactness is poor because there is only one longitudinal warp system in its structure, and the three lateral levels are prone to relative sliding, which makes the internal structure of the net damaged, and the sheet forming and dewatering effects are not good, and the cost performance is small, so it is basically eliminated at present. Two-layer and multi-layer nets seem to be fully closed from top to bottom and not easy to be dewatered, but if you tilt the net at a certain angle, you will find that the two-layer net is as smooth as the single-layer net, and its dewatering process is similar to flowing through porous objects, rather than dewatering in the vertical direction like the single-layer net, which slows down the dewatering rate to a certain extent and improves the retention of fine fibers and fillers and the evenness of the paper sheet.
Two-and-a-half-ply mesh, also known as reinforced two-ply mesh, is essentially a two-ply mesh. The two-and-a-half-ply fabric is based on the two-ply mesh with 1 group of filling weft lines added to the face layer, which can be seen from the front view and the horizontal view. The warp threads of the top layer are finer in diameter, and the correspondingly increased weft threads are finer. This structure improves the fiber support index and fiber retention rate of the net. The overall layer of the net is more compact and delicate, improving the paper-forming performance and the difference between the two sides; while the bottom weft thread diameter is much thicker than the surface weft thread diameter, ensuring better wear resistance and running stability. The two-layer half net has a wide range of application, and can be used in the production of various paper types above 300m/min on medium and high-speed paper machines, especially on medium-speed paper machines. The problem with both two-ply and two-ply fabrics is that their longitudinal single warp system remains unchanged, with the warp thread running through the weft threads of both the upper and lower layers. This on the one hand limits its potential to need to meet the different requirements of both paper and machine surfaces, and on the other hand, the weaving form of the warp threads shuttling up and down is prone to too rapid wear and tear under great tension during operation, affecting the service life of the forming fabric.

In order to solve the problems that exist in two-layer and two-and-a-half-layer nets, paper fabric workers have developed a three-layer net. The characteristic of the three-layer net is that the surface layer and the bottom layer can be completely separated, so that the surface layer becomes the paper-forming surface and the bottom layer becomes the supporting surface and wear-resistant surface. In this way, the warp and weft threads of the top layer can use finer diameter polyester monofilaments to weave a more suitable paper performance of the top layer (paper surface); the weft threads of the bottom layer can use thicker diameter polyester monofilaments, with a certain proportion of nylon instead of polyester monofilaments, so as to improve the service life of the forming network; the number of weft threads of the top layer and the bottom layer is 2:1 or 3:2. The combination of the two layers is sewn together through the middle layer. Weft stitching can be used, such as conventional three-layer mesh and self-supporting bound stitching (SSB) technology three-layer mesh.
The top and bottom layers of warp and weft are each interwoven to form separate net layers; the two layers are sewn together by a single weft yarn in the middle lateral direction, the only function of the single weft is to sew the top and bottom layers together, usually using nylon yarn. This structure of the net in the paper machine operation process, the internal wear and tear is more serious, easy to break caused by the separation of the upper and lower two layers of the net and down the machine. Therefore, the SSB type series forming net was developed, which adopts a horizontal double weft stitching system, where two adjacent stitches are interwoven in turn on the top and bottom layers, and the double stitches look like 1 line from the surface, so that the surface weave structure achieves the ideal flat weave and makes the surface flatness optimal. Compared with the traditional three-layer net, this exchange rotation of adjacent stitched weft threads in SSB net limits the relative movement of the top and bottom layers, which moderates their wear and improves their service life to a certain extent; in addition, this stitching not only plays the role of stitching the top and bottom layers, but also plays the role of supporting fibers in the top layer, making the net as a whole more compact.
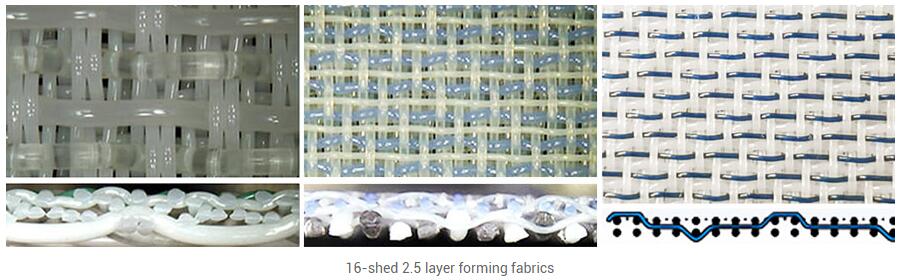
SSB nets are currently the leading products of three-layer nets, and each variety has different series. Currently, 16, 20 and 24 healds are commonly used. The so-called heald number is used to describe the different sequential arrangements of a weaving cycle on a loom, and for multi-layer nets, is calculated by looking at the upper and lower layers as a whole. The higher the number of healds, the greater the variety of weaving cycle variations. According to the current use, 16 heddle SSB net has good wear resistance, but it is easy to warp; 24 heddle SSB net is not easy to warp, but the service life is shorter than 16 heddle SSB net. In use, according to the paper type and paper machine to choose accordingly. Forming net in the paper machine in the process of running, the surface layer and the bottom layer there is a relative movement of friction, which not only on the traditional three-layer net stitching line caused wear, SSB forming, its wear and tear can not be ignored. After a period of operation, the middle binding line inside the SSB net will also be worn out, which is mainly caused by the relative motion friction between the top and bottom layers caused by the longitudinal tension during the operation of the paper machine, and the greater the load of the paper machine, the more powerful the wear. This wear not only affects the service life of the forming net, but also affects the dewatering and cleaning of the net, for example, the wear is more likely to adhere to the adhesive, etc.
Several foreign companies producing paper forming fabrics have developed products in this area, as the design of three-ply nets according to the characteristics of the paper type and paper machine can improve paper quality and paper machine efficiency.
Traditional three-layer and SSB nets are using horizontal weft stitching technology, paper machine operation, the surface and bottom layer to produce relative movement caused by wear and tear, long-term operation will damage the internal structure of the stitching yarn and surface and bottom layer. In recent years, a three-layer web with warp stitching technology has emerged, represented by the integrated binding of warp threads. It can be seen that, unlike traditional three-ply nets and SSB nets, IWB nets use warp stitch technology, which is a structural change. During paper machine operation, the warp stitch is also subject to longitudinal tension, but because the warp stitch is along the longitudinal direction of the paper machine and there is no relative movement between the upper and lower layers, there is little internal wear. This warp-stitched IWB web is tighter in structure and has increased strength when subjected to longitudinal tension during operation. This increased strength allows the use of higher quality fine yarns, higher warp and weft density, increased fiber support, and improved dewatering performance and paper quality. At present, the following three layers of polyester forming net has been eliminated by foreign advanced paper companies, the domestic high-speed paper machine is also basically used in the three-layer net, especially SSB net. IWB net and WSB net is a new forming net, IWB net in foreign countries is gradually promoted. With the increasing maturity of technology and the development of paper machine, IWB and WSB net and so on must be the dominant domestic paper forming net products.
Paper forming net is developing rapidly, the current SSB net can basically meet the market demand, and with the maturity of IWB net and WSB net technology, they will become the main dewatering equipment for high-speed modern paper machine. In order to improve the surface of the forming network and other performance, foreign countries have three and a half, or even four layer network, but the increase in the number of layers caused by the increase in the thickness of the forming network, resulting in high operating load of the paper machine, low dewatering efficiency and other problems, the loss is not worth the gain, so the prospects are not good.
Future development trend of paper forming network: (1) more adaptable to all kinds of modern high-speed, wide paper machine polyester three-layer forming network technology. This requires systematic research forming net in the process of high-speed paper machine application of wear, pollution mechanism and dewatering performance course. (2) develop and improve the three-layer polyester forming net of multi-species, multi-series products. Product development can be carried out through further improvement of the weaving process, such as analysis based on different pulp raw materials, copying methods and paper machines, and changing the warp and weft ratio of the top and bottom layers of the three-layer net. (3) Develop functional three-layer polyester forming fabrics. Such as improving the hydrophilic surface of polyester forming fabric, improving its ability to resist water-repellent resin and other adhesive pollutants; improving the abrasion resistance, stability and pollution resistance of forming fabric by adding nano polyester materials. Paper forming fabric is a cross-industry product, and these key scientific issues involve various fields and industries. The universities, research institutes and enterprises cooperate in research and development, share information and resources, and will certainly develop a series of forming fabrics for high-speed paper machines adapted to domestic.