What is Nonwoven mesh belts?
Nonwoven mesh belts, also known as nonwoven conveyor belts, are specialized belts used in the production of nonwoven fabrics. These belts are typically made from a variety of materials such as polyester, nylon, metal, conductive wire fiber and throught the air permeability of conveyor belt to match line speed that guarantee the optimum nonwoven bonding and drying process.
Nonwoven mesh belts are used in various stages of the nonwoven fabric production process, such as in the bonding, drying, and cooling stages. During the bonding stage, the nonwoven mesh belt is used to carry the fabric through a bonding oven where heat, pressure, or adhesives are applied to fuse the fibers together. In the drying stage, the belt is used to carry the fabric through a heated chamber to evaporate any remaining moisture. In the cooling stage, the belt is used to carry the fabric through a chilled chamber to cool and stabilize the fabric.
PFM Screen' s nonwoven mesh belts are designed to be durable, heat-resistant, and have a smooth surface to prevent any damage to the nonwoven fabric during production. They are available in various sizes and designs to accommodate different nonwoven fabric production processes.
The forming methods of nonwoven fabrics
Non-woven fabrics are produced by different forming methods which involve the consolidation of fibers, filaments, or films without weaving or knitting. There are several methods for forming non-woven fabrics, including:
1. Spunbonding: Spunbonding is a method of producing non-woven fabrics from thermoplastic polymers by extruding molten polymer through spinnerets to form continuous filaments, which are then laid down randomly on a moving belt or drum, and then bonded together by heat, pressure, or chemicals. This process produces fabrics with high tensile strength, dimensional stability, and breathability.
2. Meltblowing: Meltblowing is a method of forming fine fibers directly from molten polymers by forcing the polymer through a spinneret, followed by high-velocity hot air or steam, which stretches and draws the fibers to fine diameters. The fibers are then collected on a moving belt or drum, and then bonded together by heat, pressure, or chemicals. This process produces fabrics with high filtration efficiency, absorbency, and softness.
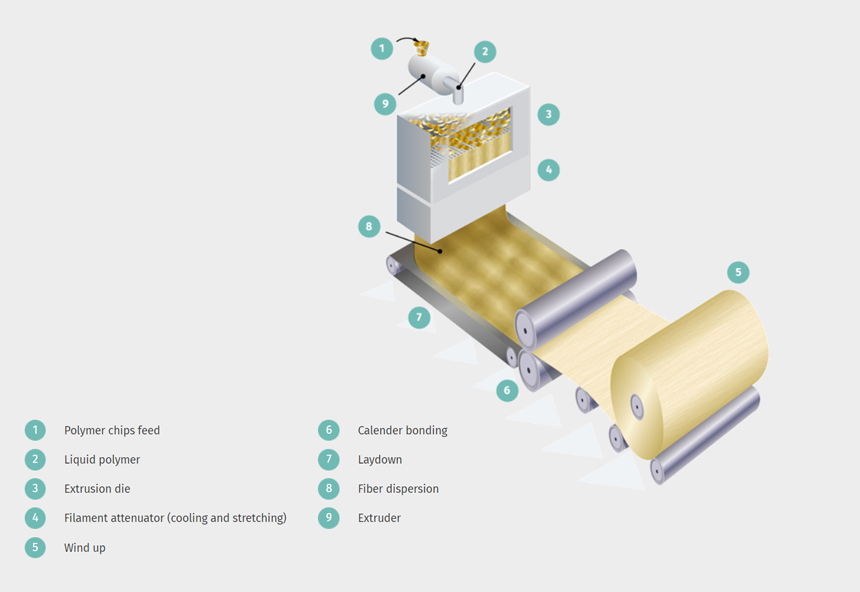
Spunlaid & Meltblown
3. Needle punching: Needle punching is a method of mechanically interlocking fibers or webs by passing a barbed needle through the fibers or web, and then withdrawing it, which causes the fibers to entangle and interlock with each other. This process produces fabrics with high loft, bulk, and resilience.
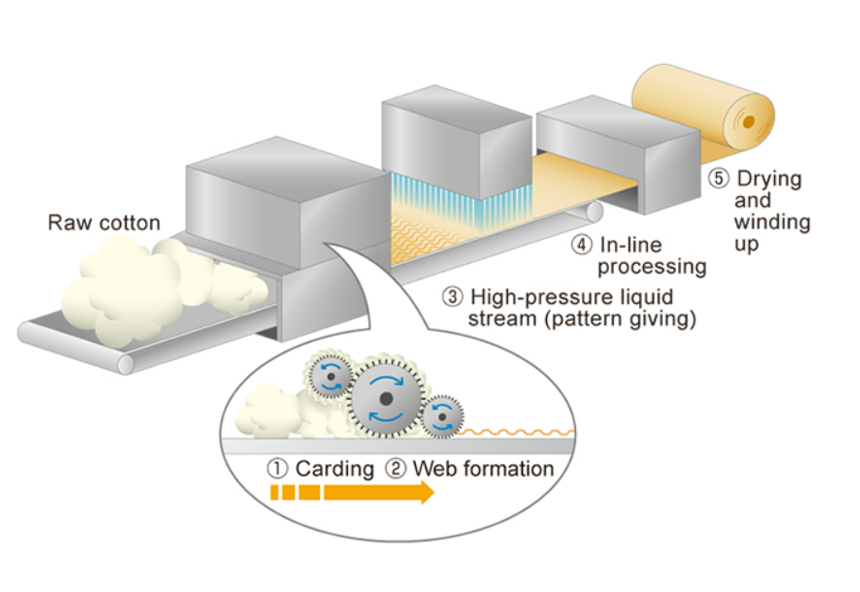
Spunlace (hydroentangling) method
4. Wet-laid: Wet-laid is a method of forming non-woven fabrics from pulp fibers or other short fibers dispersed in a water suspension. The fibers are dispersed in water and then drained onto a moving screen or belt, where they are consolidated by pressure, and then dried. This process produces fabrics with high absorbency, softness, and flexibility.
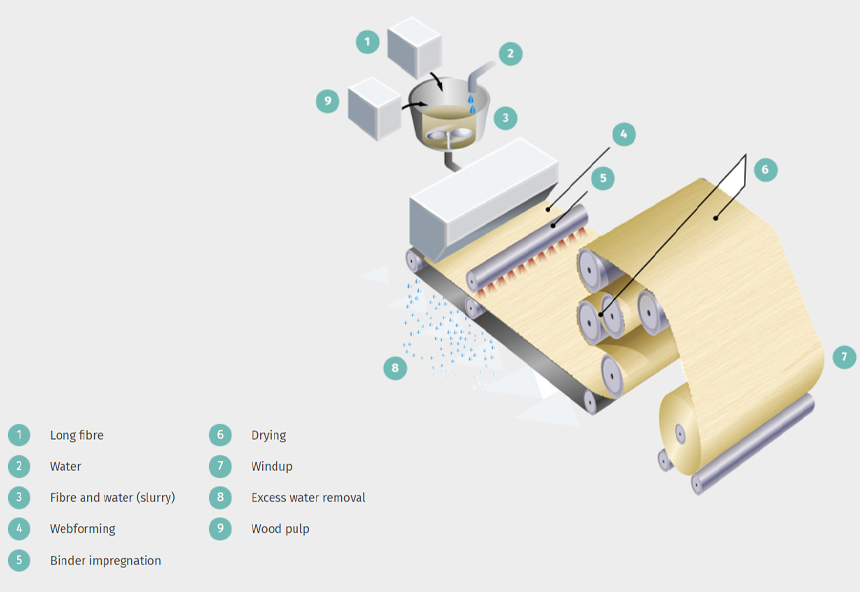
Wet-laid
5. Drylaid-carded: Carding is a mechanical process which starts from bales of fibres. These fibres are ‘opened’ and blended after which they are conveyed to the card by air transport. They are then combed into a web by a carding machine, which is a rotating drum or series of drums covered by card wire (thin strips with teeth). The precise configuration of cards will depend on the type of fibre and the basis weight to be produced. The web can be parallel-laid, where most of the fibres are laid in the machine direction, or they can be randomised. Typical parallel-laid carded webs result in good tensile strength, low elongation and low tear strength in the machine direction and the reverse in the cross direction. Machine parameters and fibre mix can be varied to produce a wide range of fabrics with different properties.
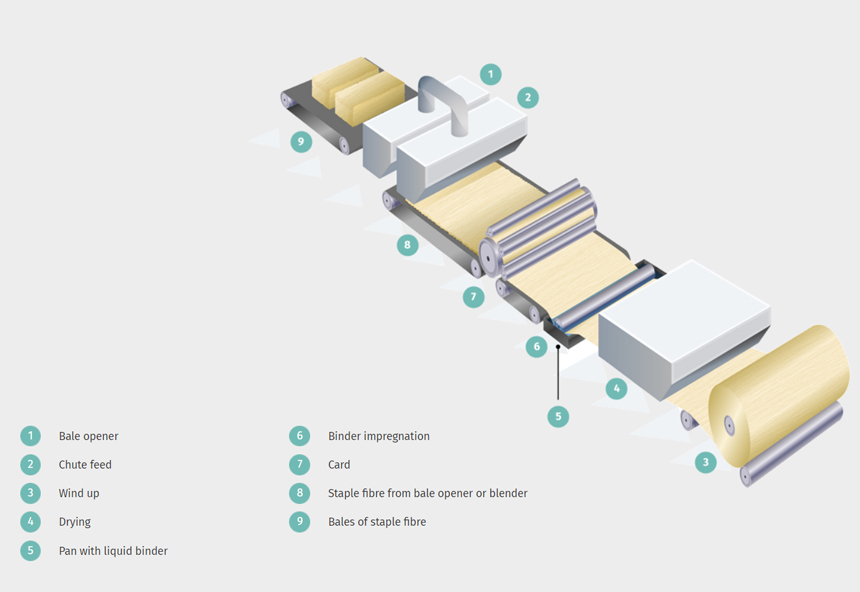
Drylaid-carded
In summary, there are several methods for forming non-woven fabrics, each with its unique advantages and characteristics. Spunbonding and meltblowing are both methods of producing non-woven fabrics from thermoplastic polymers, with spunbonding producing fabrics with high tensile strength and dimensional stability, while meltblowing produces fabrics with high filtration efficiency and absorbency. Needle punching is a mechanical method of interlocking fibers to produce fabrics with high loft and resilience, while wet-laid is a method of forming non-woven fabrics from pulp fibers or other short fibers dispersed in a water suspension to produce fabrics with high absorbency, softness, and flexibility. Finally, chemical bonding is a method of bonding fibers or webs together using chemicals to produce fabrics with high strength, durability, and stiffness.
PFM Screen offers a comprehensive range of nonwoven mesh belts
For the non-woven manufacturing process, PFM Screen offer plastic and metallic mesh belts for each step from web forming to bonding.
PFM Screen offer a range of nonwoven mesh belts for various applications, including spunbond, meltblown, and air-through bonding.
Our fabrics are made from various materials:
Polyester, polyamide, conductive yarns, PPS, stainless steel and bronze.
Weaving: up to 9 m- wide
Aperture: from 150 to 1600 CFM
Maximum speed 1,000m/min
Seams: endless woven or non marking pin seam
